The cloud is a buzzing topic for enterprises and small businesses, whether it be for building an app or infrastructure deployment. And as companies increasingly move their businesses to the cloud, it’s more important than ever to understand the different variations of cloud services.There are three models that we’re going to take a closer look at in this post; Software as a Service (SaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS). Each of these have their particular pros and cons that are important to recognize when choosing the best suited option for your organization.
To put it in context, let’s say you just started your company and you want to build your presence online. Your first initial thought is a website, but in order to host it and it’s applications, you need a IaaS product. And let’s say you want to create a custom feature, then you need a PaaS product which allows you to build custom apps with open APIs. But maybe it just got too complicated to grasp at this point, then you might want to take a look at SaaS services such as Wix that allows you to easily create website that is updated and hosted by the creator through a web browser. The only thing you need is to pay a subscription, choose a template, fill it with content – and you’re good to go!
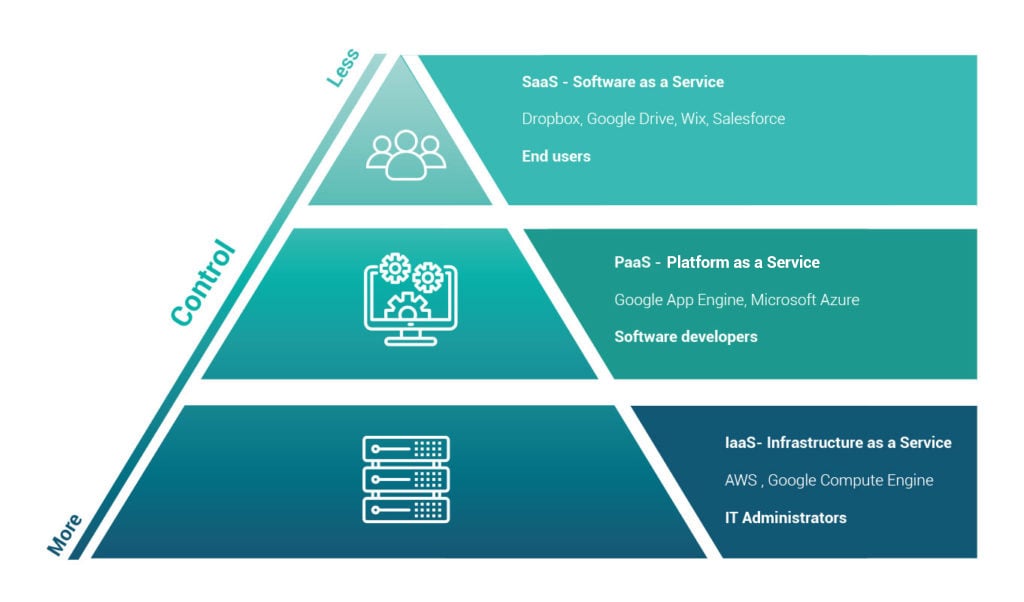
SaaS
Examples: Wix, Dropbox, Salesforce, Google drive
SaaS or Software as a Service is the most common among the cloud service options. It utilizes internet to deliver applications, which are managed and hosted by a third-party vendor. Most of the apps run directly through your web browser so you can avoid downloads or installations. Startups or small companies might see it as the best fitting solution when for example launching e-commerce. It allows users to easily create an e-commerce website for web and mobile access. You just create your website and post all your content and its basically all done. Changes can be made continuously without having to worry about server of software issues.
Who does it suit?
SaaS products are great for pretty much any type of business. A good example of this is G Suite, a collaboration tool that is universally used regardless of business size companies
- If you’re a small company that doesn’t want to focus on servers, hardware and software issues.
- For projects that require collaboration between teams
- For applications that need web and mobile access
Pros and cons:
The advantages with SaaS mainly boils down to how easy it is to set up and start using. SaaS is entirely cloud-based and is accessible at all times without having to locally host software in office. In addition, this means companies can spend less time, effort and money due to the reduced need for installations, management and upgrades. This frees up plenty of time for your organization to focus on what you do best instead of deploying your entire IT-staff to for example build a customized website.
However, easy always comes with a price tag; control. You have no control over the infrastructure it runs on, so if there is an outage, you will definitely experience it. This can result. SaaS products are also quite limited when it comes to customization and integrations unless they provide an open standard. It’s also usually a one-size-fits-all solution, that provides the same functionality, performance and integrations no matter if you company is small or big.
PaaS
Examples: Windows azure, Google app Engine, Openshift
PaaS or Platform as a Service delivers a framework for developers to build customized applications. All servers, storage and networking can be managed by the enterprise or a third-party provider while the developers can focus on managing their applications. The platform is delivered over internet and developers can avoid operating systems, software updates, storage and infrastructure. PaaS is especially suited for businesses that want custom applications but also want to reduce cots and time spent through assistance with rapid development and deployment.
Who needs it?
PaaS products are primarily targeted to companies that want to build their own apps without having to get too involved in the technical part of servers, databases and networks. It’s therefore a great alternative for developers who want to deploy and test apps without the related infrastructure.
- When you need multiple developers working within the same project.
- When you want to create a customized app
- When you don’t want to get too involved with the technical aspects of app development
Pros and cons
The PaaS model gives administrators complete control over the platform software and applications built on it. It serves as a complete framework that assist in all stages of app development such as development, testing and deployment. It’s also a highly scalable solution that can be adjusted according to business needs.
On the other hand, it doesn’t serve as completely flexible due to the fact that it may be difficult to integrate existing services and infrastructure. In addition, it’s entails risking vendor lock-in, whereas switching providers might result in data loss.
IaaS
Examples: Cisco Metapod, Microsoft Azure, Google Compute Engine (GCE)
IaaS or Infrastrucuture as a service refers to cloud-based infrastructure resources that are delivered to companies through virtualized technology. This allows roganizations to build and manage their own servers, network, operating systems, and storage. IaaS means that customers an control their own data infrastructure without having to physically manage it on-site. Instead, they can access and store data on servers through an API.
Startups and small companies may prefer IaaS to avoid spending time and money on purchasing and creating hardware and software. Larger companies may prefer to retain complete control over their applications and infrastructure, but they want to purchase only what they actually consume or need. Companies experiencing rapid growth like the scalability of IaaS, and they can change out specific hardware and software easily as their needs evolve. Anytime you are unsure of a new application’s demands, IaaS offers plenty of flexibility and scalability.
Who needs it?
If you’re looking for more control over the infrastructure, hardware and software of the solution in development – IaaS is the best alternative. It provides both increased security and far higher customization.
- If you’re a small business that wants more control of infrastructure, hardware and software
- If you’re looking for a much more customizable option
- If you want increased security
Pros and cons
IaaS cloud infrastructure offers companies and administrators the greatest level of control and power over software and hardware, but they’ll also be responsible for making sure they’re technologically secure and running properly to avoid causing outages in critical parts of your company’s operations.
The future of cloud services
Companies are moving to the cloud at fast pace, and it will result in a lot of development in the cloud services. We can expect to see more SaaS companies take place in the market with interesting new services and technologies. Cloud integration has also been one of the challenges with moving to the cloud, and this has resulted in a need for reliable integrations. iPaaS is set to be the next step in PaaS development that serves as a platform where developers can build and implement integration solutions in the cloud. However, while all of these are fairly new terms, modern solutions will take over what we know as cloud services today and unify what IaaS, SaaS and PaaS deliver individually. New modern solutions will be able to integrate all into one holistic infrastructure with streamlined process flows.
After reading this we hope we’ve made the pretty complex decision a little easier for you. It can also come down to investing in 2 of the models if you’re looking for a specific solution. For example, you might want SaaS for project management, but want PaaS to build an app.